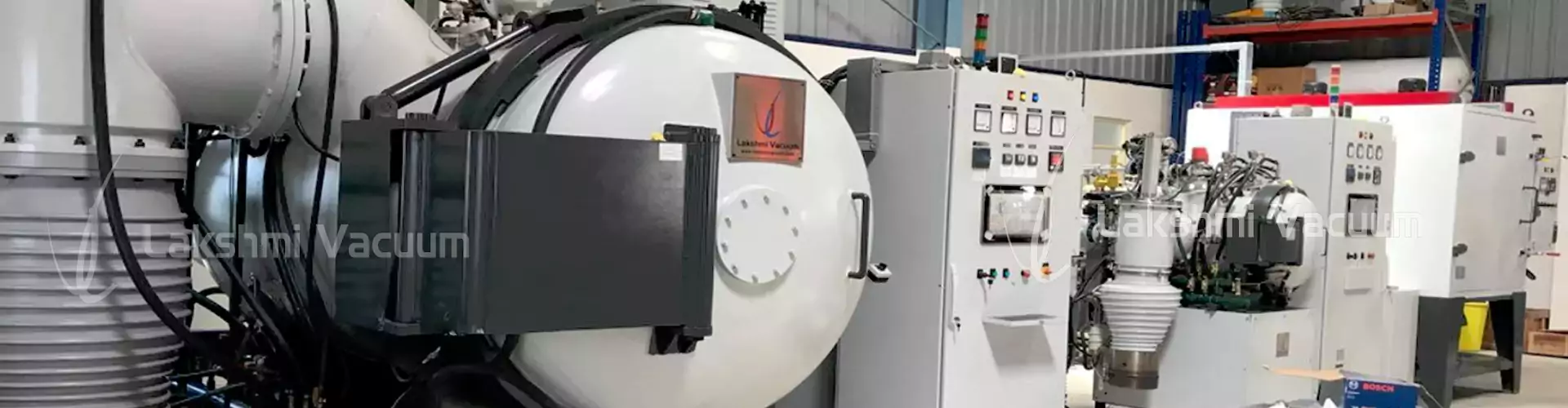


Vacuum Brazing Furnace
Definition: A furnace used to join dissimilar metals using a filler material under vacuum, ensuring clean, strong, and flux-free joints.
Working: Components are heated above the filler’s melting point in a vacuum chamber, allowing capillary action to bond parts without oxidation.
| S.No. | Parameter | Technical Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Useful working area | 900 x 900 x 1200mm/ Customizable |
| 2 | Maximum Temperature | 1250°C |
| 3 | Hot Zone | Graphite/All metal |
| 4 | Vacuum level | 1 X 10-2 mbar (1 X 10-6 if required) |
| 5 | Charge weight | 900 kg |
| 6 | Furnace Vessel | Carbon Steel/SS |
| 7 | Maximum Quenching Pressure | 6/10/12 bar |
| 8 | No. of Zones | 1 or 3 Zones Dependable |
| 9 | Power supply | Heavy duty 415V AC, 50Hz three phase |
| 10 | Control System | PLC, IPC with SCADA |
| 11 | Application | Joining of stainless steel, aerospace parts, copper, etc. |
| 12 | Cooling System | High-pressure inert gas quenching (N₂ / Ar) |

Vacuum Sintering Furnace
Definition: A furnace that densifies powder materials by heating them below their melting point under vacuum or controlled atmosphere.
Working: Metal or ceramic powders are compacted and sintered in a high-temperature vacuum to create strong, high-density components without contamination.
| S.No. | Parameter | Technical Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Useful working area | 900 x 900 x 1200mm/ Customizable |
| 2 | Maximum Temperature | 1250°C - 2000°C |
| 3 | Hot Zone | Graphite |
| 4 | Vacuum level | 1 X 10-2 mbar (1 X 10-6 if required) |
| 5 | Charge weight | 900 kg |
| 6 | Furnace Vessel | Carbon Steel/SS |
| 7 | Maximum Quenching Pressure | 6/10/12/15 bar |
| 8 | No. of Zones | 1 or 3 Zones Dependable |
| 9 | Sintering Atmosphere | Vacuum / Argon |
| 10 | Power supply | Heavy duty 415V AC, 50Hz three phase |
| 11 | Control System | PLC, IPC with SCADA |
| 12 | Application | Powder metallurgy, ceramics, carbide tools, CMCs |
| 13 | Cooling System | Water-cooled with optional gas quenching |

Vacuum Hardening Furnace
Definition: A furnace that hardens steel and alloys by heating under vacuum and rapidly cooling using high-pressure gas quenching.
Working: The material is heated to austenitizing temperature in vacuum, then quenched with inert gas to achieve hardness and structural transformation.
| S.No. | Parameter | Technical Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Useful working area | 900 x 900 x 1200mm/ Customizable |
| 2 | Maximum Temperature | 1250°C |
| 3 | Hot Zone | Graphite/All metal |
| 4 | Vacuum level | 1 X 10-2 mbar (1 X 10-6 if required) |
| 5 | Charge weight | 900 kg |
| 6 | Furnace Vessel | Carbon Steel/SS |
| 7 | Maximum Quenching Pressure | 6/10/12/15 bar or oil quench |
| 8 | No. of Zones | 1 or 3 Zones Dependable |
| 9 | Power supply | Heavy duty 415V AC, 50Hz three phase |
| 10 | Control System | PLC, IPC with SCADA |
| 11 | Application | Tool steels, dies, aerospace parts, precision components |
| 12 | Cooling System | High-pressure inert gas quenching (N₂ / Ar) |

Vacuum Degassing Furnace
Definition: A specialized furnace for removing dissolved gases (like hydrogen or oxygen) from molten or solid metals.
Working: The furnace heats metals under deep vacuum, allowing trapped or dissolved gases to escape, improving material purity and properties.
| S.No. | Parameter | Technical Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Useful working area | 900 x 900 x 1200mm/ Customizable |
| 2 | Maximum Temperature | 800°C – 1600°C (depending on material) |
| 3 | Hot Zone | Graphite/All metal |
| 4 | Vacuum level | 1 X 10-4 mbar (1 X 10-6 if required) |
| 5 | Charge weight | 900 kg |
| 6 | Furnace Vessel | Carbon Steel/SS |
| 7 | Gas Removal | Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen degassing |
| 8 | No. of Zones | 1 or 3 Zones Dependable |
| 9 | Power supply | Heavy duty 415V AC, 50Hz three phase |
| 10 | Control System | PLC, IPC with SCADA |
| 11 | Application | Purification of molten metals (steel, alloys, superalloys) |
| 12 | Cooling System | Water-cooled coil and walls |

Vacuum Carburizing Furnace
Definition: A thermal treatment furnace that introduces carbon into the surface of steel under vacuum using hydrocarbon gases.
Working: The component is heated in vacuum and exposed to carburizing gas, allowing carbon atoms to diffuse into the surface, followed by rapid gas quenching.
| S.No. | Parameter | Technical Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Useful working area | 900 x 900 x 1200mm/ Customizable |
| 2 | Maximum Temperature | 1250°C |
| 3 | Hot Zone | Graphite/All metal |
| 4 | Vacuum level | 1 X 10-2 mbar (1 X 10-6 if required) |
| 5 | Charge weight | 900 kg |
| 6 | Furnace Vessel | Carbon Steel/SS |
| 7 | Maximum Quenching Pressure | 10/12/15/20 bar or oil quench |
| 8 | No. of Zones | 1 or 3 Zones Dependable |
| 9 | Power supply | Heavy duty 415V AC, 50Hz three phase |
| 10 | Process gass | Hydrocarbon gases like: Acetylene, Propane, Methane. |
| 11 | Control System | PLC, IPC with SCADA |
| 12 | Application | Gear parts, transmission components, tool steels |
| 13 | Cooling System | High-pressure inert gas quenching (N₂ / Ar) |

Vacuum Melting Furnace
Definition: High-purity melting system using electromagnetic induction.
Working: A metal charge in a crucible is heated by an induction coil while vacuum removes gases and prevents contamination during melting.
| S.No. | Parameter | Technical Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Melting Capacity | 1 kg – 500 kg |
| 2 | Crucible Material | Graphite / Alumina / Zirconia |
| 3 | Induction Frequency | 1–10 kHz (adjustable) |
| 4 | Vacuum level | 1 × 10-4 mbar |
| 5 | Max Temperature | Up to 1700°C |
| 6 | Cooling System | Water-cooled induction coil and chamber walls |
| 7 | Alloy Capability | Ferrous / Non-ferrous / Reactive metals |
| 8 | Degassing Feature | Optional inert gas purging |
| 9 | Control System | PLC, IPC with SCADA |
Definition: Suitable for reactive or refractory metal processing.
Working: Under high vacuum or inert gas, an arc is struck to melt high-melting-point or reactive metals for button or ingot formation.
| S.No. | Parameter | Technical Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Melting Capacity | 100 g – 2 kg |
| 2 | Electrode Diameter | 10 – 100 mm Suitable |
| 3 | Crucible Material | Graphite / Alumina / Zirconia |
| 4 | Atmosphere | Argon / High Vacuum |
| 5 | Vacuum level | 1 × 10-6 mbar |
| 6 | Max Temperature | Up to 3500°C |
| 7 | Cooling System | Water-cooled copper hearth |
| 8 | Arc Ignition | Manual / Automatic Arc Starter |
| 9 | Power supply | DC power supply |
| 10 | Applications | Titanium, Zirconium, Tantalum etc.. alloys |
| 11 | Number of Buttons | Single or Multi-button capability |
| 12 | Control System | PLC, IPC with SCADA |

Vacuum Ovens
Definition: Used for drying, curing, and aging materials in vacuum conditions.
Working: The oven heats samples gently while vacuum lowers boiling points, enabling safe and uniform drying or curing of heat-sensitive items.
| S.No. | Parameter | Technical Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Temp Range | Ambient to 250°C / 400°C (depending on model) |
| 2 | Vacuum Level | 10-3 - 10-5 mbar |
| 3 | Chamber Size | 25L – 500L |
| 4 | Heating System | Uniform electric heaters with PID control |
| 5 | Material | SS304/SS316 interior |
| 6 | Shelves | Adjustable / Removable |
| 7 | Controller | Digital PID / Programmable touchscreen |
| 8 | Arc Ignition | Manual / Automatic Arc Starter |
| 9 | Applications | Drying, Degassing, Curing, Baking |
| 10 | Control System | PLC, IPC with SCADA |

Vacuum Autoclaves
Definition: Pressure vessels for composite curing or sterilization.
Working: Materials are loaded into the chamber, then vacuum and temperature cycles are applied to bond layers or sterilize without air entrapment.
| S.No. | Parameter | Technical Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chamber Size | Customizable: Ø300 mm – Ø2000 mm x 700mm L – 6000mm L |
| 2 | Max Pressure | Up to 10 bar (gas) |
| 3 | Max Temperature | Up to 250°C |
| 4 | Vacuum Level | 10-3 mbar |
| 5 | Heating Method | Electrical / Steam jacket |
| 6 | Door Type | Manual / Hydraulic locking |
| 7 | Applications | Composite curing, Sterilization, Bonding |
| 8 | Power Supply | 380–480V, 3-phase, 50Hz |
| 9 | Pressurizing rate | 0.5 to 1 bar/min Dependable |
| 10 | Depressurizing rate | 0.5 to 1 bar/min Dependable |
| 11 | Control System | PLC, IPC with SCADA |

Thermo Vacuum Chambers
Definition: Simulate space conditions for aerospace component testing.
Working: The chamber reaches ultra-high vacuum while internal heaters/coolers simulate thermal extremes, replicating conditions of outer space.
| S.No. | Parameter | Technical Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Internal Size | Customizable (based on payload/test size) |
| 2 | Temperature Range | -80°C to +150°C (or higher on request) |
| 3 | Vacuum Level | 10-6 m.bar |
| 4 | Temperature Uniformity | ±2°C |
| 5 | Material | SS304/316 with mirror finish |
| 6 | Instrument Ports | Customizable (feedthroughs, viewports) |
| 7 | Cooling System | LN2 / Thermal circulators |
| 8 | Heating System | Electric / Infrared heating |
| 9 | Applications | Space Simulation, Aerospace Testing, Outgassing |
| 10 | Control System | PLC, IPC with SCADA and (DAS) Optional |

Vacuum Hot Press
Definition: A high-temperature pressing system that combines heat and uniaxial pressure under vacuum to densify powders or bond materials.
Working: Materials are heated in a vacuum chamber while hydraulic pressure is applied to consolidate or bond them, ensuring high-density and defect-free parts.
| S.No. | Parameter | Technical Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Max Temperature | Up to 2200°C (graphite/molybdenum heaters) |
| 2 | Max Pressure | Up to 100 tons (hydraulic press) |
| 3 | Heating Zone Size | Ø100 mm to Ø600 mm (custom sizes available) |
| 4 | Vacuum Level | 10-3 - 10-5 m.bar |
| 5 | Atmosphere Capability | Vacuum / Inert gas (Argon, Nitrogen) |
| 6 | Control System | PLC, IPC with SCADA and (DAS) Optional |
| 7 | Heating Type | Resistance heating with multi-zone control |
| 8 | Cooling System | Water-cooled components |
| 9 | Applications | Powder sintering, diffusion bonding, composite pressing |

Low Pressure Nitriding Furnace
Definition: A Low Pressure Nitriding Furnace is a heat treatment system that diffuses nitrogen into the surface of metals under vacuum or low pressure to enhance hardness, wear, and fatigue resistance.
Working: The furnace heats parts to 450–700°C in a low-pressure nitrogen-rich atmosphere, allowing nitrogen atoms to penetrate the surface and form a hard nitride layer without surface oxidation.
| S.No. | Parameter | Technical Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Useful working area | 900 x 900 x 1200mm/ Customizable |
| 2 | Maximum Temperature | 700°C |
| 3 | Hot Zone | Graphite/All metal |
| 4 | Vacuum Level | 1 * 10-2 mbar |
| 5 | Charge weight | 900 kg |
| 6 | Furnace Vessel | Carbon Steel/SS |
| 7 | Temperature Uniformity | ±5°C (AMS 2750) |
| 8 | No. of Zones | 1 or 3 Zones Dependable |
| 9 | Power supply | Heavy duty 415V AC, 50Hz three phase |
| 10 | Process gass | Ammonia (NH₃) and/or Nitrogen + Hydrogen |
| 11 | Control System | PLC, IPC with SCADA |
| 12 | Application | Automotive Gears, Aircraft Landing Gear, Injection Molds |
| 13 | Cooling System | Gas cooling (Nitrogen, Helium) |
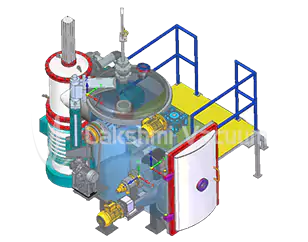
Vacuum Strip Casting Furnace
Definition: A Vacuum Strip Casting Furnace is a specialized system used to melt and rapidly solidify high-temperature alloys into thin metal strips under vacuum or controlled atmosphere.
Working: The alloy is induction-melted in a vacuum chamber and cast onto a water-cooled copper wheel, enabling fast solidification into uniform, high-quality strips.
| S.No. | Parameter | Technical Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Melting Capacity | 1 – 10 kg (Customizable) |
| 2 | Cooling Method | Copper Wheel with Internal Water Cooling |
| 3 | Casting Atmosphere | High Vacuum / Inert Gas (Ar, N2) |
| 4 | Furnace Temperature | Up to 1600°C |
| 5 | Strip Thickness | 20 – 200 microns |
| 6 | Strip Width | Up to 100 mm |
| 7 | Control System | PLC with Touchscreen HMI |
| 8 | Vacuum Level | ≤ 1 x 10⁻³ mbar |

Pack Aluminizing Furnace
Definition:A Pack Aluminizing Furnace is a high-temperature system used for diffusion coating components with aluminum to enhance their resistance to oxidation and corrosion.
Working: Components are buried in an aluminum-containing powder mix and heated in the furnace, causing aluminum vapors to diffuse into the surface and form a protective aluminide layer.
| S.No. | Parameter | Technical Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Maximum Temperature | 1150°C |
| 2 | Heating Method | Electric (Kanthal/MoSi2/SiC Heaters) |
| 3 | Furnace Type | Box / Pit / Retort Type |
| 4 | Furnace Temperature | PLC with HMI |
| 5 | Atmosphere | Air / Inert Gas (Optional) |
| 6 | Insulation | Ceramic Fiber Modules |
| 7 | Chamber Size | Customizable |
| 8 | Temperature Uniformity | ±5°C across hot zone |



Our operations adhere to international quality and saftey standards, with certifications and procedures in place to support customer-specific audits and technical evaluations.





